SECTION 1 – NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALS
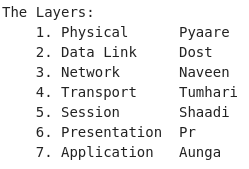
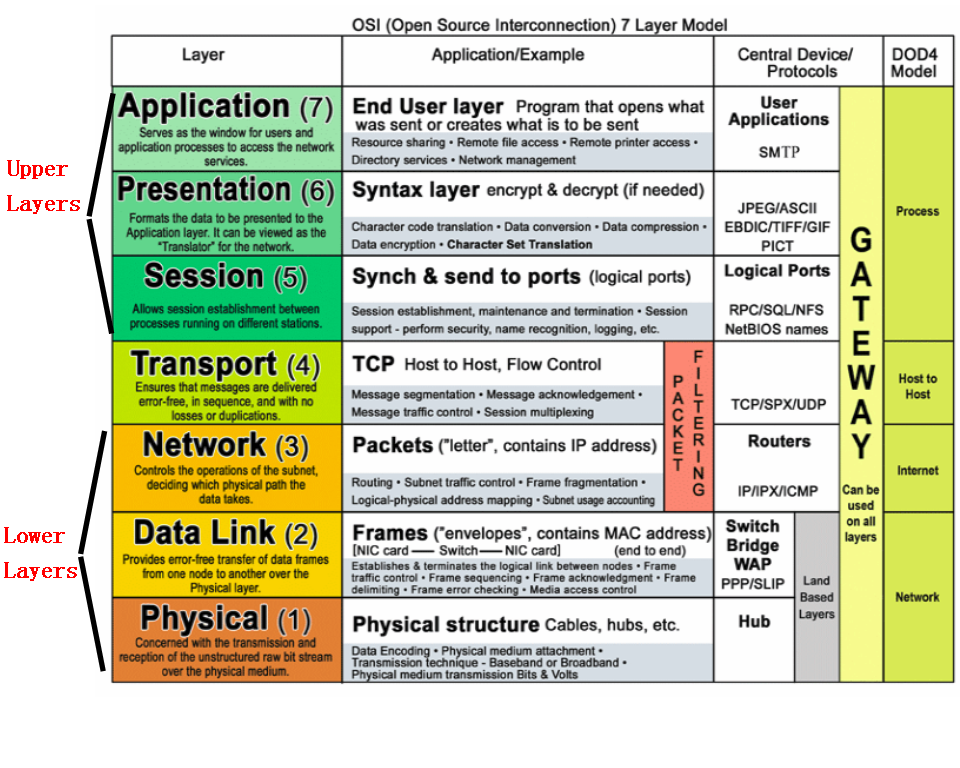
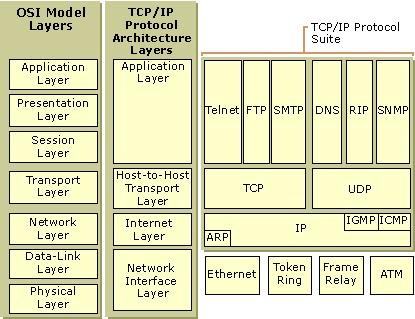
OSI MODEL – OPEN SYSTEM INTERCONNECTION MODEL
Compromise of 7 layers and explain how data transfer takes place.
There are unique protocols at every layer.
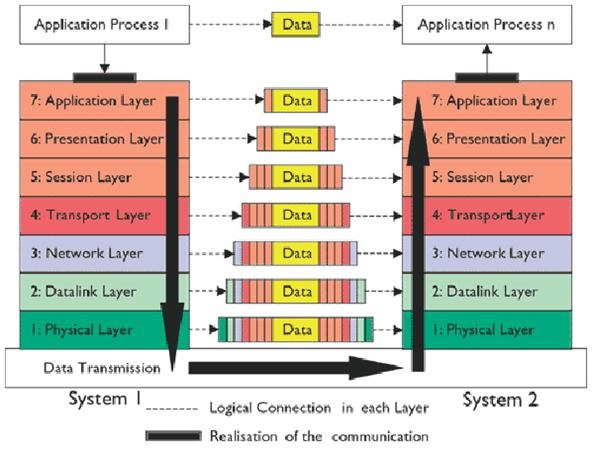
Each layer enclose data from another layer to facilitate data transmission.
After the data reaches to the destination the reverse process (unpacking) happens.
Each layer is in charge of some kind of processing and each layer only talks to the layers immediately below and above it.

Each layer will add or remove control information that it is in charge of.
Summary of Layer 1 and 2
When a network card receives a stream of bits over the network, it receives the data from the wires (the first layer), then the second layer is responsible for making sense of these 1s and 0s. The second layer first checks the destination MAC address in the frame to make sure the data was intended for that computer. If the destination MAC address matches the MAC address of the network card, it carries on.
Layer 5: Session
The session layer manages the setting up and taking down of the association between two communicating end points, called a connection. A connection is maintained while the two end points are communicating back and forth.
It's in this layer that ports are used and that data is properly directed.

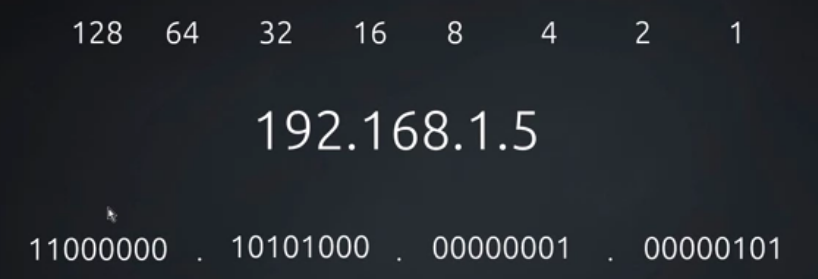
IP Address:
[Layer 3, Routing]
Unique Address of a device on a network.
Structure:
They are composed of octets (range 0 to 255).
An octet is a group of eight binary digits (0,1).
[1 = on , 0 = off]
Ex: 192.168.1.5

when IP address is combined with a subnet mask,we can calculate the network subnet(LAN) to which the host belongs to.
Subnet masks accompany an IP address and the two values work together.
Netmask tells us how many IP address we can have.
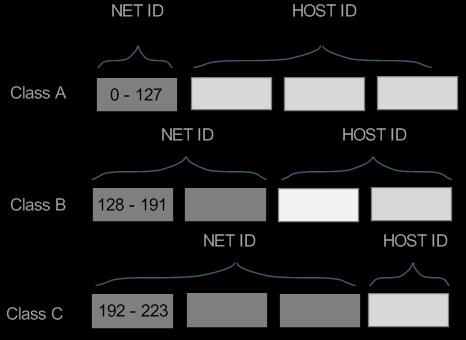
Applying the subnet mask to an IP address splits the address into two parts, an extended network address(network portion of the address), and a host address.
Subnet masks contain two parts: the left side with all mask bits set to 1 (the extended network portion) and the right side with all bits set to 0 (the host portion).
Example- 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000 = 255.255.255.0
A bit value of 11111111 is equal to 255.
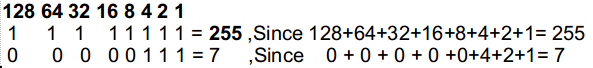
Position with 255 means we are completely locked out but other than 255 it means we have flexibility.
In the example 24 bits are turned on therefore we have “/24” network here which means We can not change the first 24 bits of the network.
Example in 192.168.134.x , 192.168.134 is fixed and 'X' can be anything from 0 to 255
-
255 - The value of 255 is never used as an address for any part of the IP address. It is reserved for broadcast addressing.
Ex: There are 256 hosts(addresses available) in '/24'.
But first adn last address are reserved
Broadcast address - last address - 192.168.1.255
Network ID address - first address - 192.168.1.0
Therefore only 254 addresses out of 256 are available. -
Most popular subnet masks:

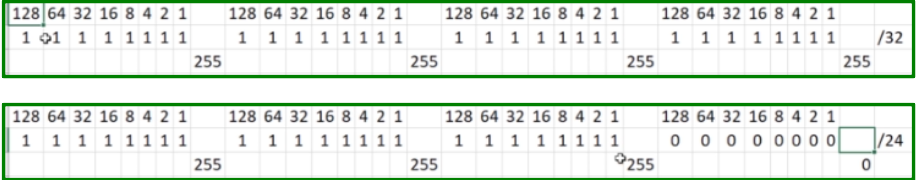
Number of IP Addresses available:
IPv4 = 2^32
IPv6 = 2^128
- We have IPv6 but we do not use it, we still use IPv4 Thanks to NAT(Network Address Translation).
Types Of IP Addresses:
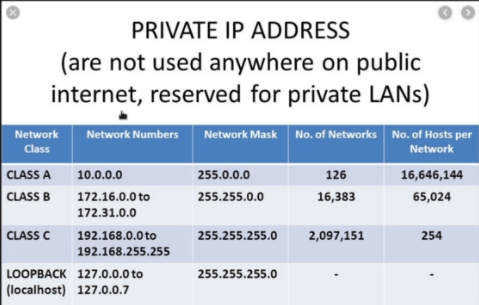
1. Private IP
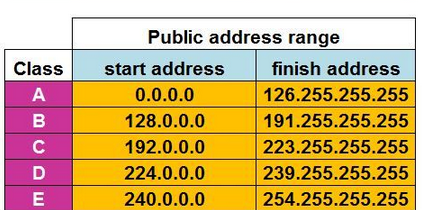
2. Public IP (Rent/Purchase from ISP)
Broadcast Address
A subnet has only 254 addresses instead of 256 because two of the address are used up by default on every subnet:the subnet number and broadcast address
Subnet number-first number in subnet range identifies the subnet.Ends with .0
Broadcast address-last address on the subnet.Ends with .255
Mac Addresses
[Layer 2, Switching]
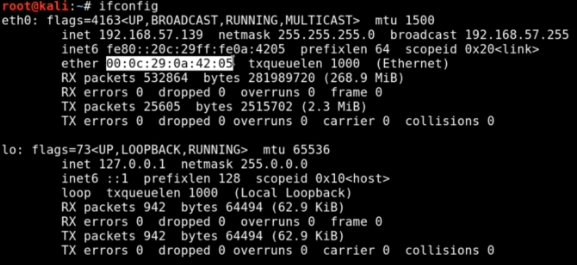
Here,
inet = IPv4
inet6 = IPv6
ether = MAC addresses(Physical Address)
Media Access Control Address helps in identifying a unique host on a network.Used by switches to know what device is what.
MAC Address-Layer 2-Data Link Layer
IP Address-Layer 3-Network Layer
It is associated with NIC(Network Interface Card).
They are globally unique.
48 bits length and 12 hexadecimal characters.
First 6 of 12 chars are assigned to different organizations.This part is called OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier).
First 3 Pairs are identifiers (identify manufacturers)
Ex: 00:0c:29 = VMware Inc.
Router is a layer 2/3 device since it does both routing and switching.
ARP
Address Resolution Protocol-the mechanism that bridges gap between IP and MAC Addresses.
Networking devices and computers keep ARP Tables that match IP Addresses to MAC Addresses.
ARP table is used when data is shared within same subnet.
If destination IP is not in the same subnet the data is forwarded to default gateway.
If there is no MAC in Arp table,the host will send an ARP broadcast on the subnet using subnet's broadcast address to every host - asking who owns the IP Address?
Basic information about network interfaces:
Windows - ipconfig /all
Linux - ifconfig
Contents of ARP cache: arp -a
TCP/IP Ports & Protocols
A port is a way to tag different types of traffic.
Well known ports and protocols:

- Firewall block or permit certain types of traffic based on ports.
TCP vs UDP
[Layer 4,Transportation Layer]
TCP
- Transmission Control Protocol
- Connection Oriented Protocol
- High Reliability
- Utilised by http/s,ssh,ftp
- Works on 3-way handshake SYN>SYN-ACK>ACK
UDP
- User Datagram Protocol
- Connection Less Protocol
- Utilised by VoIP,DNS,Streaming Services
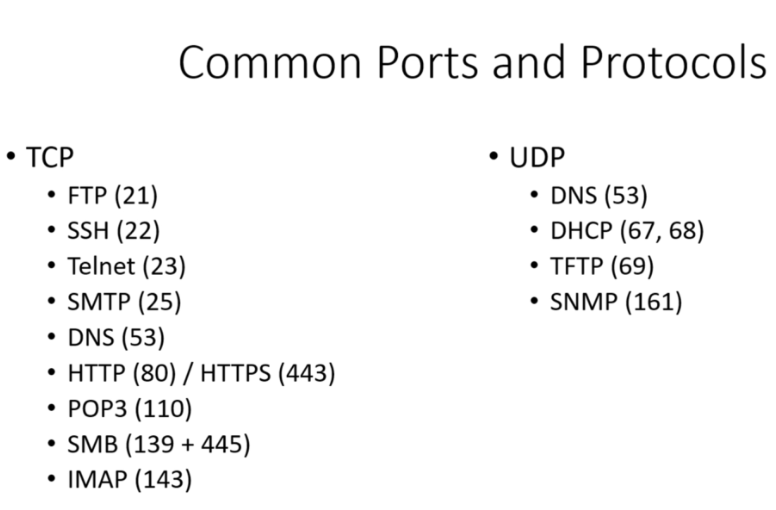
Protocols Info
- Telenet - used for remote login
- SSH - Encrypted version of telenet
- SMB - samba -file sharing
- DHCP - associate IP Address
- TFTP -Trivial FTP utilises UDP instead of TCP
- SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol
If you want to troubleshoot network start from Physical Layer.
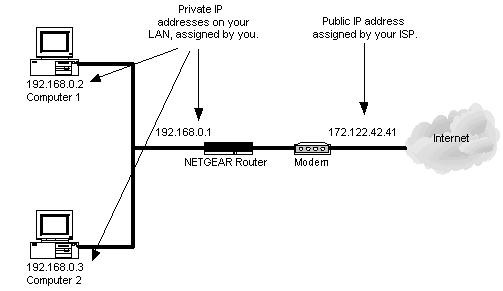
One day there will not be enough IP Addresses to support the number of devices.Therefore the idea of private networks and NAT came into existence.
Range of private IP Address:

192.168.1.0 - most common default network assigned to home routers.
Device on private network cannot reach internet unless an intermediary device performs NAT or Network Address Translation.
NAT - swaps one hosts ip address for another ip address.
Multiple private address can share the same public IP address.
Devices on private network behind NAT firewall are hidden from the public internet.
Ports
When referring to a network or the Internet, a software or network port is a location where information is sent.
- A port number is always associated with an IP address of a host and the protocol type of the communication.
- For example, port 80 is the http network port.
There are a total of 65,535 ports. - Each of which is either Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port types, there are some ports which are both TCP and UDP types.